How to filters your data
Filters allow you to only return rows or apply operations on rows that match certain conditions.
The actions
Fetch, Update, Delete and RPC offers two ways to define filters.Note: You have the option to use either one method or both, as the filters will be
combined for the final query to your Supabase instance. The choice is yours.
Method 1 - Using the filters dropdown
This is easiest and the recommanded way to define filters on your actions.
You can define up-to 5 filters to apply on your query.
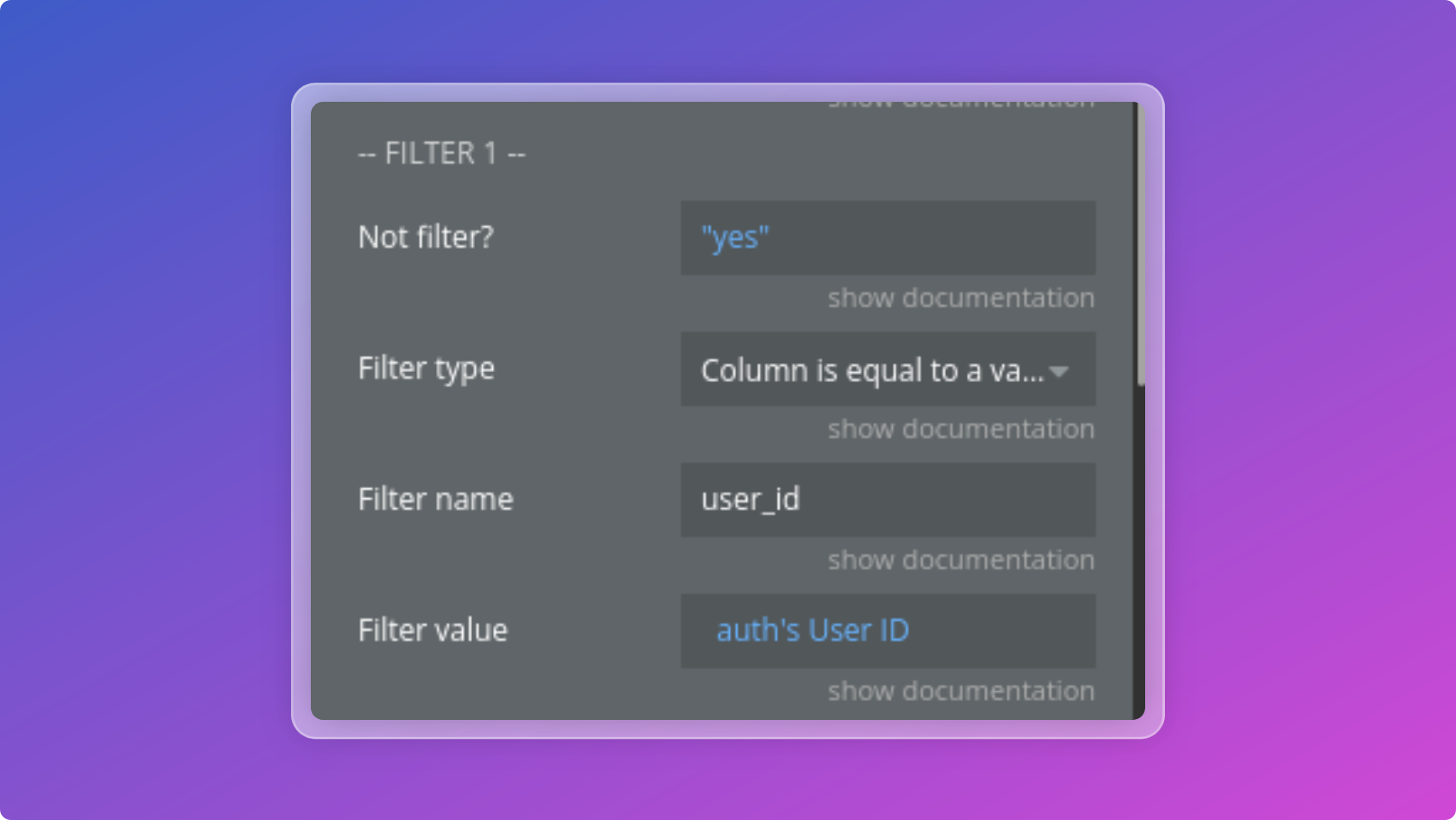
You can choose the filters combination with:
Title | Description | Type |
Filter Combination | Select "AND" (default) to apply all filters simultaneously, or "OR" to match any single filter. | Dropdown |
Not filter? | Match only rows which doesn't satisfy the filter | Yes/No |
Filter type | The filter to apply | Dropdown |
Filter name | The name of the column to filter on | Text |
Filter value | The value of the filter | Text |
Method 2 - Using Advanced filters
Apply any Supabase filter operators directly to your query by specifying a list of filters.
You can chain filters by placing one per line.
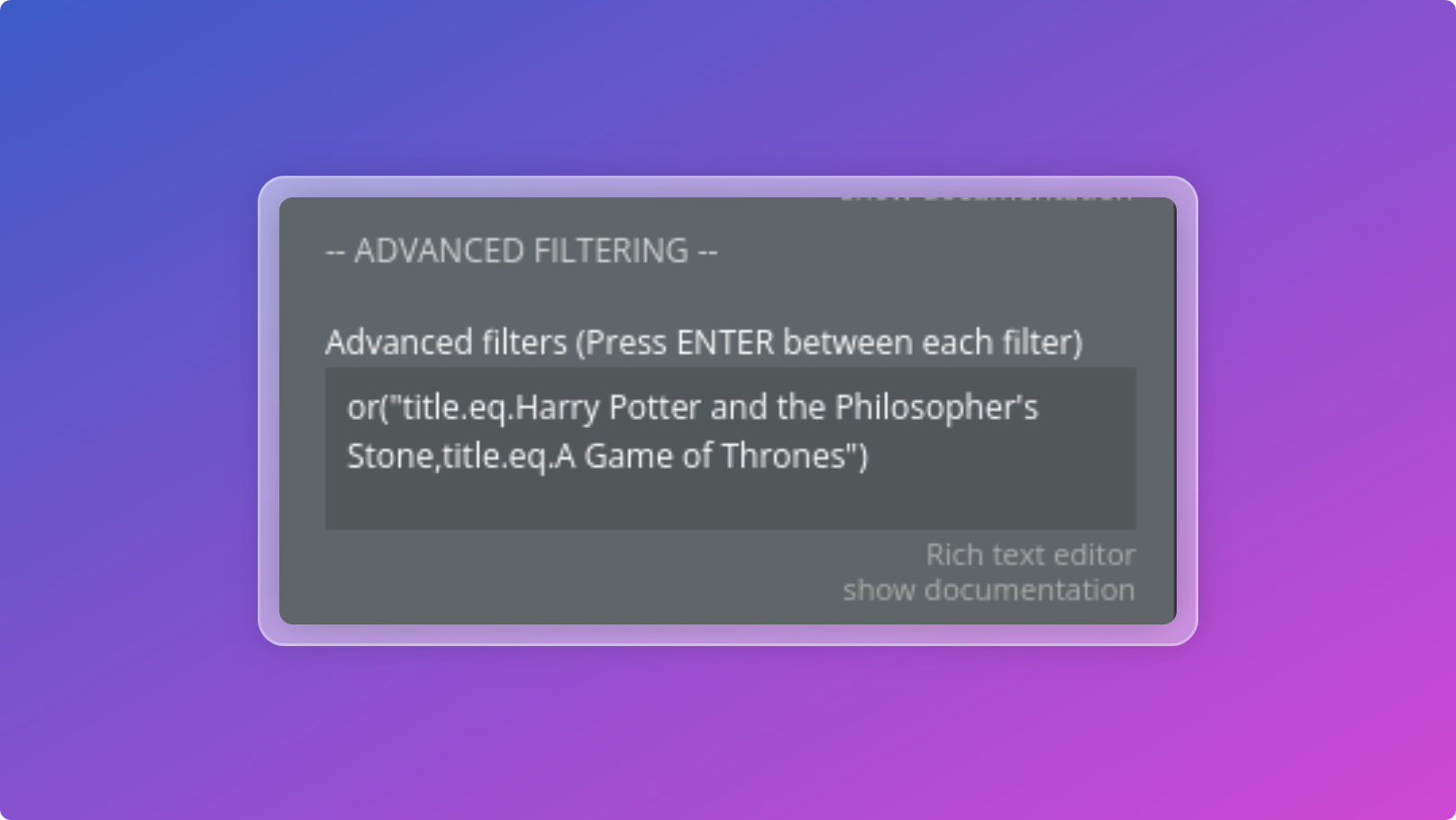
Examples:
jsoneq("title", "Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone")
jsoneq("author_id", 1)
jsoneq("author_id", 2) like("title", "%Thrones%")
jsonilike("title", "%Harry Potter%")
jsonor("author_id.eq.1,title.like.%Kings%")
jsonin("author_id", [1, 2])
jsonor("title.eq.Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone,title.eq.A Game of Thrones")
jsonor("title.like.%Chamber%,title.like.%Orient%")
